Ethereum: How Interest and Fractional Reserve Banking Could Work in a Limited Money Supply
As we navigate the complexities of a limited money supply in the digital age, it’s essential to consider how alternative financial systems like Ethereum could potentially function. One intriguing concept that has gained significant attention is interest and fractional reserve banking. In this article, we’ll explore how these principles might work in an economy with a limited monetary supply.
What are Fractional Reserve Banks?
Fractional reserve banking is a type of banking system where depository institutions (banks) require only 10% of their deposits to be held in reserve and issue the remaining 90% as loans. This allows banks to extend credit more freely, as they don’t need to hold much physical cash on hand.
Interest-Backed Loans
Now, let’s introduce interest-backed loans into our scenario. Suppose Bitcoin lenders (banks, creditors, investors) issue loans with a fixed interest rate. As the total supply of bitcoins approaches 21 million, the lending institution will receive an increasing number of loan requests, leading to a larger demand for loans.
How Would Interest and Fractional Reserve Banking Work in a Limited Money Supply?
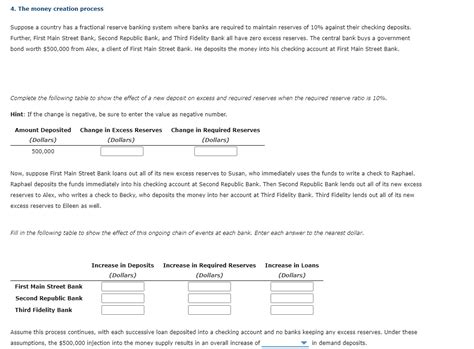
In a limited money supply economy, interest-backed loans could work as follows:
- Increased demand for loans: With a growing economy, people’s incomes might increase, driving up demand for loans from banks.
- Higher borrowing costs: As the total supply of bitcoins approaches 21 million, lenders may need to raise their lending rates (interest) to maintain profitability, while borrowers may face higher borrowing costs due to increased competition and liquidity constraints.
- Increased economic activity: Higher interest-backed loan rates could stimulate economic growth by encouraging borrowing and investment, as individuals and businesses seek to finance new ventures or upgrade existing assets.
- Fractional reserve banking implications: If the economy is growing rapidly, a fractional reserve banking system could work to accommodate increased credit demand. Lenders might offer more loans with lower interest rates, while also maintaining their 10% reserve requirements.
Potential Limitations and Concerns
While interest-backed loans can stimulate economic growth, there are potential limitations and concerns:
- Risk of asset bubbles: Increased lending activity could lead to asset price bubbles, as borrowers may take on excessive debt to invest in assets like real estate or stocks.
- Systemic risk: A large number of fractional reserve banks might create systemic risk if the overall economy experiences a downturn, leading to widespread bank failures and financial instability.
- Inefficient allocation of credit: Interest-backed loans could lead to inefficient allocation of credit, as lenders focus on lending to those who can afford it, rather than targeting more productive investments.
Conclusion
Interest-backed loans in a limited money supply economy could work by increasing borrowing costs and stimulating economic growth through increased activity. However, this system also introduces potential risks and concerns, such as asset bubbles and systemic risk. To mitigate these challenges, alternative financial systems like Ethereum might be designed with built-in safeguards, such as:
- Centralized lending pools: Using blockchain technology to create a centralized lending pool, allowing for more efficient allocation of credit and reduced risk.
- Dynamic interest rates: Implementing dynamic interest rates that adjust based on market conditions to minimize the impact of asset price bubbles.
- Regular economic monitoring: Establishing regular economic monitoring mechanisms to detect potential systemic risks early and take corrective action.

Deixe um comentário Cancelar resposta